Relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K), Reaction Quotient (Q) and Gibbs Energy (G)
Relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K), Reaction Quotient (Q) and Gibbs Energy (G): Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K), Reaction Quotient (Q) and Gibbs Free Energy Change (ΔG),,, etc.
Important Questions on Relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K), Reaction Quotient (Q) and Gibbs Energy (G)
The Haber’s process for the formation of at is . Which of the following is the correct statement?
A schematic plot of ln versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
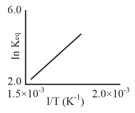
The reaction must be –
The value of equilibrium constant for a reversible reaction is , If the reaction quotient for the same reaction is , predict the direction of equilibrium reaction.
In a one-litre flask, moles of undergoes the reaction . The progress of product formation at two temperatures (in Kelvin), and , is shown in the figure:
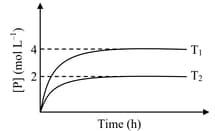
If and , then the value of is
[ and are standard Gibb's free energy change for the reaction at temperatures and , respectively.]
The value of for the reaction at is (Nearest integer)
Given:
(Taken )
Derive the relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K), Reaction Quotient(q) and Gibbs Energy(G).
Give the relationship between equilibrium constant (k), reaction Quotient (Q), and Gibbs energy (G)
For a sponatneous reaction the value of must be negative, and the value of must be greater than _____
(Given )
What is the (approx) partial pressure of at equilibrium at ?
at for substance in liquid state and gaseous state are and , respectively.
Vapour pressure of liquid at is approximately equal to: .
What is the of the following reaction?

Which of the following is not true for the above equilibrium?
Which of the following options will be correct for the stage of half completion of the reaction ?
At of is dissociated to . What is the approximate standard Gibbs free energy change at and pressure for this process? .
The Haber’s process for the formation of at is . Which of the following is the correct statement?
Select the correct option about for the following reaction
(Given: , molar volume of water at )
for the reaction
the thermodynamic equilibrium constant at is:
Which of the following is correct at equilibrium?
Select the graph which can be used to determine standard free energy of the reaction given below:
Assume that the reaction is at equilibrium.
Among the following set of conditions, which condition necessarily holds true for a non-feasible process?
(Where, equilibrium constant)
